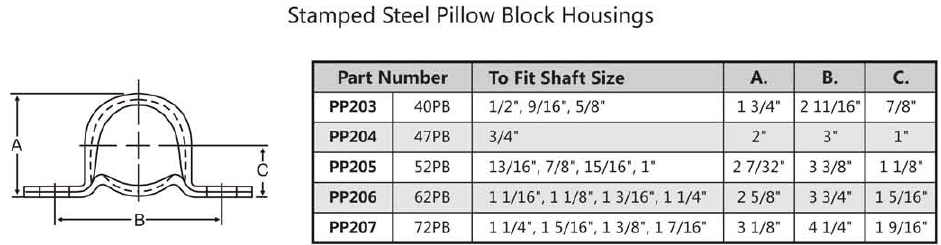
Magnetic iron ore with vanadium and titanium as raw material factory direct production of V 2 O 5 are mainly in South Africa, Finland and Australia and other countries vanadium plant. Vanadium in vanadium-titanium magnetite mainly replaces iron in spinel with the same type of isomorphism, but vanadium-titanium magnetite varies from mineralization to mineralization. First, Finland The Altamaki mine in Finland's Lautaruji contains 40% magnetite, containing 0.25% to 0.3% V. Vanadium is present in the titanium magnetite crystal lattice. The ore is first magnetically removed to remove the gangue, and then finely ground to 0.1 ~ 0.2mm, wet magnetic separation to obtain vanadium magnetite concentrate, the composition is as follows: Composition V Fe TiO 2 SiO 2 % 0.65 69.5 1.8 0.5 The process is characterized by the use of pellets in the shaft furnace for sodium oxide roasting. A pellet of 10 to 12 mm was prepared by adding 3% to 6% of soda ash, and the furnace was kept at 1200 ° C for about 11 hours. Cooled to 600 ~ 700 ° C out of the furnace. Dip in water for 36h. The vanadium leaching rate is greater than 95%. Al 2 (SO 4 ) 3 was added to remove silicon, and the supernatant was added with ammonium sulfate to precipitate ammonium polyvanadate. The pellet after leaching is used as a raw material for iron making. Musta Walla was the new base discovered by the company in 1962 and was completed and put into production in 1976. The ore contains Fe 17% and V 0.2%. The process is basically similar to that of Ortamaki. The total recovery of vanadium is 77%. The vanadium precipitation rate is 99.8%, with an annual output of V 2 O 5 3kt. The finished ingredients are as follows: Finished product V 2 O 5 V 2 O 4 Fe 2 O 3 SiO 2 Na 2 O K 2 O NH 3 H 2 O Ammonium vanadate /% 90 0.6 0.02 0.1 0.1 0.1 5.6 3.2 Foil /% 92 6.0 0.05 0.15 0.1 0.1 Second, South Africa The Bushweed igneous rock in Transvaal, South Africa, has about 2 billion tons of vanadium-titanium magnetite. The main ore layer contains about 1.5% V 2 O 5 , 54% to 60% Fe and 12% to 14% TiO 2 . (1) The Witbank vanadium plant in Transvaal Its raw materials are as follows: ingredient Fe V 2 O 5 TiO 2 Al 2 O 3 Cr 2 O 3 % 50~60 ~2.5 8~20 1 to 9 ~1.0 The production process is shown in Figure 1. The ore is ground to 70%-200 mesh, dehydrated, and added with soda ash, salt, and thenardite , oxidized and calcined at 1200 ° C in a rotary kiln. The discharged HCl gas is first sprayed with water, then neutralized with ammonia, and subjected to cyclic absorption, and NH 4 Cl reaches 150 to 180 g/L, and is used as a vanadium sinking agent. The calcined material has a large specific porosity and is leached by percolation with water. The leachate was subjected to precipitation of vanadium with NH 4 Cl to obtain ammonium metavanadate. Ammonium metavanadate was dried at 50 ° C and was white crystals and sold as a product. Further calcination and deamination to obtain red vanadium oxide as a catalyst. Further melting, can be made into a fuse sold, the ingredients are as follows: ingredient V 2 O 5 Na 2 O SiO 2 Fe As P S Ammonium metavanadate /% 77.1 0.1 0.1 0.05 0.01 0.01 0.01 Red vanadium oxide foil /% 99.3 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.01 0.01 0.01 Figure 1 South Africa Witbank plant process From ore to product, the total yield of vanadium is about 60%. After the vanadium-vanadium solution is evaporated and concentrated, NaCl can be precipitated, and the NH 4 Cl mother liquor can be returned to use. (2) Gaspracks factory in Middelburg The plant was commissioned in 1974. The Bushweed mine is also used as a raw material. The ingredients (%) are as follows: ingredient V Fe TiO 2 SiO 2 % 0.92 55.6 12.7 2.2 The ore is firstly crushed to 30mm, dried, and then ground to 70%-0.09mm. Glauber's salt is added and granulated with Na 2 SO 4 to give a particle size of 10 to 12 mm. It is first dried on a grate machine, preheated to 900 ° C, and then calcined at 1270 ° C for 60-110 min in a rotary kiln, and the conversion rate is greater than 92%. It is believed that the use of V 5 + in the liquid reflux to catalyze the calcination can promote the conversion of trivalent vanadium and thenardite in the ore to soluble V 2 O 5 . The SiO 2 in the ore has a significant effect on the vanadium leaching rate. It can be seen from 2 that SiO 2 is more than 2.5%, which has obvious adverse effects. The combination of alkali and silicic acid increases with increasing temperature and time. Figure 2 Effect of silicon oxide on vanadium leaching rate 1- Add 7% Na 2 SO 4 ; 2 - Add 14% Na 2 SO 4 The calcined pellets are leached by countercurrent in the large-scale leaching tower connected in series, and the temperature has a significant influence on the leaching rate, as shown in FIG. Increasing the temperature to 125 ° C can significantly shorten the leaching time. Figure 3 Effect of leaching temperature on vanadium leaching rate The obtained leach solution contains 35 to 70 g/LV, about 1 g/L SiO 2 , and the suspension is 3 to 7 g/L. Al 2 (SO 4 ) 3 was added in addition to silicon in an amount of 1.2 mol per mol of SiO 2 . When adding vanadium, the amount of (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 is 1.2 mol per mol of V 2 O 5 , pH=7.5-9, and the temperature is 25-35 ° C, and the obtained ammonium metavanadate contains Na 2 O less than 0.1%. Decomposed in a rotary kiln and melted into V 2 O 5 fuses for sale. After the direct oxidation of sodium vanadium-magnesium magnetite to roasting, when the leaching residue contains high sodium, it is not suitable for use as ironmaking raw material, or can only be partially used as ironmaking raw material, which is a major shortcoming of this method. Stamped Steel Pillow Block Housings Pillow Block Housing, Stamped Steel Pillow Block Housings NingBo Greenly Machinery Co.,LTD , https://www.greenlyagparts.com